IT leaders often face a “black box” problem regarding strategic alignment. Teams ship code rapidly and manage complex infrastructure, yet business outcomes remain stagnant or undefined. This disconnect wastes budget and burns out top engineering talent who cannot see their impact.
You must bridge the gap between technical execution and company-wide strategy. This urgency explains why 75% of companies rate corporate strategy as the essential driver for adopting OKRs to increase revenue through defined goals and business strategies.
In this guide, we provide actionable frameworks and specific IT OKR examples to fix this alignment gap. We focus on moving from tracking activity to measuring concrete value. The following strategies ensure your technology roadmap drives revenue, efficiency, and security.
Key Takeaways
- Outcomes over outputs: Shift focus from “features shipped” to adoption rates and performance metrics.
- Align technical debt: Connect code refactoring directly to customer satisfaction to justify the engineering time.
- Cadence matters: Avoid the “set and forget” trap by implementing strict bi-weekly progress check-ins.
- Leading indicators: Prioritize metrics like deployment frequency rather than relying solely on lagging indicators like uptime.
- Balance innovation: Mix stability goals with aggressive innovation targets to prevent system stagnation or fragility.
What Are IT OKRs?
IT OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) link technical execution to broader business strategy. They are not a simple to-do list or a project roadmap. An Objective defines a qualitative, ambitious goal for the technology department. Key Results act as the quantitative evidence of completion.
This framework moves teams away from measuring activity to measuring value. It clarifies exactly how server uptime, code quality, or security patches impact the bottom line. Effective OKRs answer “why” we are building specific features before writing a single line of code.
Also read: Best Tools for OKR Management and Visualization
Understanding the definition is the first step; next, you need a reliable process to draft them.
Simple Steps To Write IT OKRs
Writing effective goals requires moving beyond standard KPI tracking. You need a structured approach to ensure technical efforts drive business value.
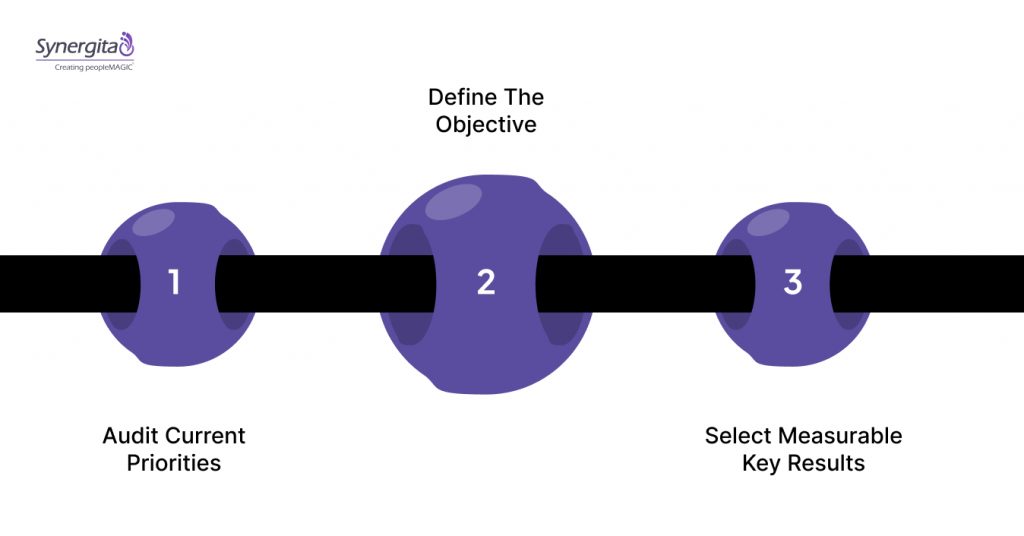
Follow these steps to draft high-impact IT OKRs:
Step 1: Audit Current Priorities
Review your current project backlog against company-wide quarterly goals. Identify which technical initiatives directly support revenue, retention, or efficiency. Discard or delay tasks that lack a clear business connection.
Step 2: Define The Objective
Write a qualitative statement that inspires the engineering team. It should describe a desired end-state, not the tasks to get there. Keep it aggressive but achievable within the quarter.
Step 3: Select Measurable Key Results
Choose three to five metrics that prove you met the objective. Focus on outcomes like “reduce latency by 20%” rather than “install new server.” Ensure these metrics are verifiable and time-bound.
Also read: Essential OKR Dashboard Examples for Goal Tracking
Now that you understand the drafting process, let’s look at concrete templates you can adapt for your team.
Top 15 IT Objectives And Key Results
Generic goals like “keep the lights on” do not drive performance or innovation. The following examples cover diverse IT functions, from cybersecurity to DevOps transformation.
Here are 15 IT OKR examples structured for immediate application:
1. Accelerate Product Delivery Speed
Objective: Improve the speed and reliability of software deployment.
| Key Result | Target |
| Deployment Frequency | Increase from bi-weekly to on-demand. |
| Lead Time for Changes | Reduce from 5 days to 24 hours. |
| Change Failure Rate | Maintain under 5% during acceleration. |
2. Strengthen Cybersecurity Posture
Objective: Establish a Zero Trust architecture to secure enterprise data.
| Key Result | Target |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Achieve 100% adoption across all internal apps. |
| Critical Vulnerabilities | Patch all critical CVEs within 48 hours of detection. |
| Phishing Simulation | Reduce employee click rate on test emails to <2%. |
3. Optimize Cloud Infrastructure Costs
Objective: Reduce cloud spend without sacrificing system performance.
| Key Result | Target |
| Unused Resources | Identify and terminate 100% of idle instances. |
| Monthly Cloud Bill | Reduce total spend by 15% via reserved instances. |
| Resource Utilization | Increase average CPU utilization to 60%. |
4. Enhance System Reliability
Objective: Deliver 99.99% uptime for core customer-facing services.
| Key Result | Target |
| Mean Time To Recovery (MTTR) | Decrease from 60 minutes to 15 minutes. |
| Incident Response | Automate initial response for 80% of alerts. |
| Service Level Objectives (SLOs) | Define and monitor SLOs for top 5 services. |
5. Modernize Legacy Systems
Objective: Migrate critical workflows away from the legacy mainframe.
| Key Result | Target |
| Data Migration | Move 100% of customer data to the new SQL cloud database. |
| Legacy Dependencies | Retire 3 major legacy application dependencies. |
| User Cutover | Transition 50% of internal users to the new interface. |
Also read: Effective OKR Examples for Teams and Businesses
6. Improve Data Accessibility
Objective: Democratize data access for non-technical business units.
| Key Result | Target |
| Self-Service Dashboards | Launch 5 new dashboards for Sales and Marketing. |
| Query Response Time | Reduce average data query time by 30%. |
| Data Catalog | Document and index 100% of core data warehouses. |
Ready to implement these IT OKRs? Book a demo to see how Synergita’s templates and tracking can accelerate your goal-setting process.”
7. Minimize Technical Debt
Objective: Improve code quality to enable faster future development.
| Key Result | Target |
| Code Coverage | Increase test coverage from 60% to 85%. |
| Refactoring | allocate 20% of sprint capacity to refactoring tasks. |
| Bug Backlog | Reduce the count of critical bugs by 50%. |
8. Upgrade Internal IT Support
Objective: Deliver a superior support experience for remote employees.
| Key Result | Target |
| Ticket Resolution Time | Reduce average resolution time to under 4 hours. |
| CSAT Score | Increase internal IT satisfaction score to 4.8/5. |
| Self-Help Knowledge Base | Create 20 new articles addressing top recurring issues. |
9. Ensure Compliance and Governance
Objective: Achieve full readiness for the upcoming SOC2 audit.
| Key Result | Target |
| Access Controls | Review and certify 100% of user access privileges. |
| Policy Documentation | Update and publish all 12 required security policies. |
| Vendor Risk | Complete security assessments for all Tier 1 vendors. |
Also read: Tips and Best Practices for OKR Reporting
10. Scale QA Automation
Objective: Shift testing left to catch bugs earlier in the cycle.
| Key Result | Target |
| Automated Test Cases | Increase automated regression suite from 40% to 80%. |
| Manual Testing Time | Reduce manual testing hours per release by 60%. |
| Defect Leakage | Decrease production defects by 25%. |
11. Enhance Mobile App Performance
Objective: Provide a faster, crash-free experience for mobile users.
| Key Result | Target |
| App Launch Time | Reduce average startup time to under 2 seconds. |
| Crash Rate | Maintain crash-free sessions at >99.9%. |
| App Store Rating | Improve average rating to 4.7 stars. |
12. Improve API Ecosystem
Objective: Build a robust API layer for partner integrations.
| Key Result | Target |
| API Documentation | Achieve 100% coverage in Swagger/OpenAPI specs. |
| Partner Integration Time | Reduce partner onboarding time from 2 weeks to 2 days. |
| API Latency | Maintain p95 latency under 200ms. |
13. Foster an Innovation Culture
Objective: Explore new technologies to drive future competitive advantage.
| Key Result | Target |
| Proof of Concepts (POCs) | Deliver 3 POCs using AI or Machine Learning. |
| Hackathons | Organize 1 internal hackathon with 80% team participation. |
| Tech Talks | Host monthly knowledge-sharing sessions. |
14. Optimize Disaster Recovery
Objective: Ensure business continuity in case of catastrophic failure.
| Key Result | Target |
| Recovery Point Objective (RPO) | Reduce data loss risk to under 15 minutes. |
| Recovery Time Objective (RTO) | Ensure systems are back online within 2 hours. |
| DR Drills | Conduct and pass one full-scale failover drill. |
15. Streamline Onboarding
Objective: Enable new engineers to ship code on day one.
| Key Result | Target |
| Environment Setup | Automate dev environment setup to under 30 minutes. |
| Documentation Review | Audit and update 100% of “Getting Started” guides. |
| First Commit | Ensure 100% of new hires deploy to staging in week 1. |
Also read: OKR vs KPI: Key Differences and How to Use Both
Having good examples is not enough; you also need the right execution strategy to ensure adoption.
Best Practices For Effective OKR Management
Even well-written OKRs fail without a supportive culture and execution discipline. You must treat goal management as an ongoing process, not a one-time event.
Implement these practices to ensure OKR success:
1. Focus on outcomes over output
Do not confuse “shipping a feature” with “solving a user problem.” Measure the result of the code, such as user adoption or latency reduction. This shifts the mindset from factory production to value creation.
Why it matters:
- Stops the “feature factory” cycle where teams build unused tools.
- Connects engineering efforts directly to revenue and customer satisfaction.
- Empowers developers to solve problems creatively rather than just closing tickets.
2. Review progress bi-weekly
Set a recurring cadence to review Key Results with your team. This highlights blockers early and allows for course correction before the quarter ends. Waiting for the end of the quarter guarantees failure.
Why it matters:
- Catches red flags and resource gaps while there is time to fix them.
- Keeps the team accountable and focused on high-priority metrics.
- Prevents the “set and forget” mentality that renders goal-setting useless.
Struggling to implement these practices across distributed IT teams? Book a demo to see how Synergita automates OKR tracking and alignment.
3. Keep goals flexible
Business priorities change rapidly in the technology sector. If a company goal shifts, update your IT OKRs immediately to maintain alignment. Rigid adherence to outdated goals wastes resources.
Why it matters:
- Allows rapid response to market shifts or critical security incidents.
- Ensures resources always target the most current business needs.
- Reduces team frustration by removing targets that are no longer relevant.
Manual tracking often undermines even the best practices; a dedicated platform simplifies this entire lifecycle.
Streamline OKR Management With Synergita
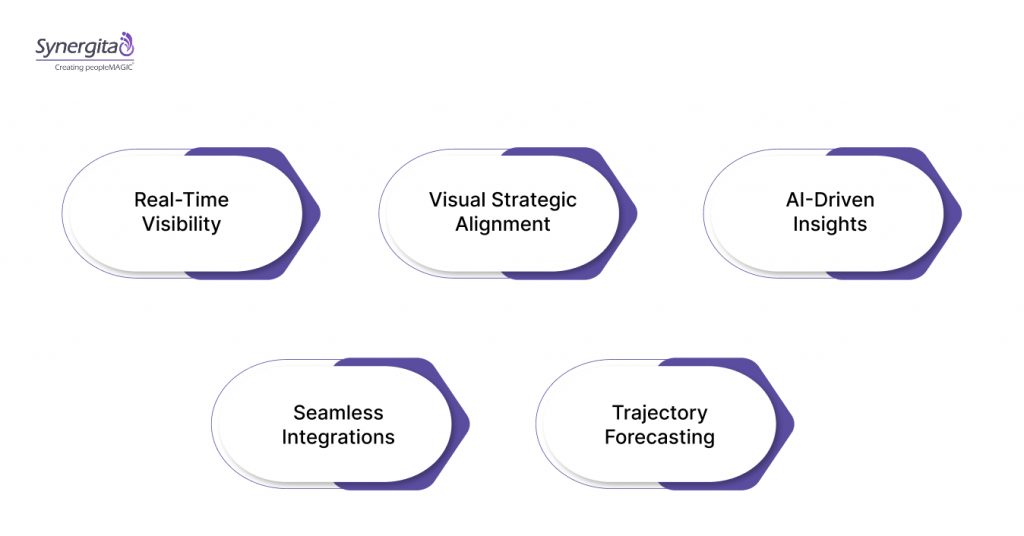
Synergita’s OKR management software transforms planning into results. Our platform connects goals to daily work and provides real-time visibility. This ensures your IT organization stays aligned and accountable.
- Real-Time Visibility: Real-time progress tracking with intuitive dashboards and automated reminders.
- Visual Strategic Alignment: Visual alignment tools that show how IT goals support business objectives.
- AI-Powered Support: AI-powered analytics that provide actionable insights free from distracting metrics.
- Seamless Integrations: Seamless integration with Microsoft Teams and Slack for continuous updates.
- Trajectory Forecasting: Automated progress tracking that highlights actual versus expected trajectories.
Synergita simplifies the entire OKR lifecycle from creation to completion. This enables your IT organization to focus on execution rather than administration.
Conclusion
IT OKRs bridge the gap between code commits and revenue targets. We explored how to draft them and reviewed 15 concrete examples. Implementing this framework shifts your team from order-takers to strategic partners.
This alignment is crucial for survival in a competitive market. You now have the playbook to drive measurable business impact through technology. Synergita simplifies this transition by automating tracking and visualization. We help you move away from annual reviews toward agile performance management.
Synergita’s OKR platform provides this essential foundation. It brings clarity and accountability to your goal-setting process. Book a demo now to start translating your IT strategy into measurable business impact today.
FAQs
Q. How do we differentiate between operational metrics and transformational OKRs in IT?
Operational metrics maintain business-as-usual activities like system uptime. OKRs should focus on strategic changes and improvements. If a goal represents maintaining current performance, it belongs in KPIs. If it drives meaningful change, it qualifies as an OKR.
Q. What specific challenges do IT teams face when implementing OKRs?
IT departments often struggle with quantifying technical work’s business impact. Infrastructure upgrades or security enhancements require creative metrics. Many technical leaders also face resistance from teams accustomed to task-based tracking rather than outcome-focused measurement.
Q. How should we handle OKRs for maintenance-focused IT teams?
Even operational teams need strategic objectives. Focus on efficiency gains, automation opportunities, or quality improvements. Examples include reducing manual work through automation or improving vendor management effectiveness rather than simply maintaining systems.
Q. What’s the realistic timeframe for seeing OKR results in IT organizations?
Most IT OKRs work effectively on quarterly cycles. Infrastructure projects may require longer timelines. Begin with pilot teams to demonstrate quick wins. Full cultural adoption typically requires 2-3 quarters of consistent practice and refinement.
Q. How do we balance between innovation and operational OKRs?
Allocate 60-70% of OKRs to core operational improvements. Reserve 30-40% for innovation and transformation goals. This balance ensures stability while driving strategic advancement. Adjust ratios based on your organization’s current transformation priorities.
Q. What happens when technical dependencies block OKR progress?
Identify cross-team dependencies during OKR planning sessions. Establish clear service level agreements between teams. Include dependency resolution as a key result when necessary. Escalate persistent blockers through formal governance channels.
Q. How specific should technical key results be for non-technical stakeholders?
Key results must demonstrate business value while maintaining technical credibility. Include both technical metrics and business outcomes. For example, pair “reduce API response time” with “improve customer transaction completion rate” to show a comprehensive impact.



