Have you ever felt like your team is working hard but not making significant progress? In 2024, global employee engagement rates fell to just 21%, resulting in a loss of around $438 billion in productivity for businesses.
Much of this stems from unclear or misaligned goals; when objectives are vague, rarely revisited, or disconnected from broader priorities, focus and motivation naturally decline.
That’s where practical goal setting in performance management comes in. In this blog, you’ll learn how to set goals that actually guide your team, promote alignment, and drive real results, so you can stop guessing and start seeing impact.
Key Takeaways:
- Goal Clarity & Alignment: Vague or misaligned goals reduce focus and motivation; clear, structured objectives drive meaningful results.
- SMART & OKRs: Measurable, time-bound goals improve performance, accountability, and team alignment.
- Balanced Approach: Combining outcome-oriented and output-oriented goals ensures effort translates into impact.
- Continuous Review: Regular check-ins, feedback, and progress tracking refine goals and sustain productivity.
- Practical Application: Structured goals across roles, from customer service to product development, turn strategy into measurable outcomes.
- Challenge Management: Obstacles like unrealistic targets or poor planning can be overcome with structured workarounds and analytics.
- AI Support: Platforms like Synergita provide actionable insights, track OKR progress, and simplify goal management.
Core Elements of Successful Goal Setting
Effective goal setting isn’t just about writing down targets; it’s about creating objectives that are clear, actionable, and aligned with both individual and organizational priorities. At its core, successful goal setting provides direction, motivates performance, and creates a framework for tracking progress.
The following components are essential to make goals truly effective:
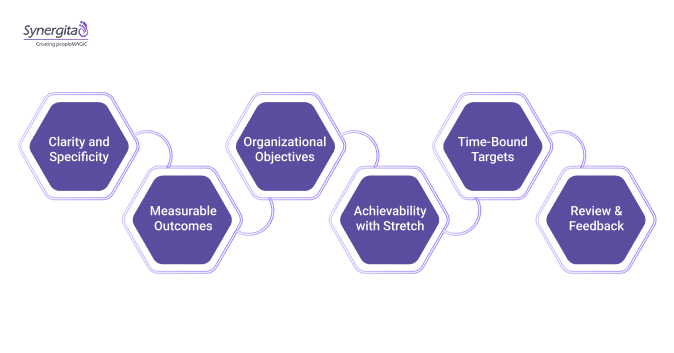
- Clarity and Specificity – Goals should be well-defined and unambiguous, so everyone knows exactly what success looks like.
- Measurable Outcomes – Include concrete metrics or indicators to track progress and assess achievement.
- Alignment with Organizational Objectives – Individual and team goals should directly support broader company priorities to ensure focus and cohesion.
- Achievability with Stretch – Goals should challenge employees while remaining realistic, striking a balance between ambition and attainability.
- Time-Bound Targets – Set clear deadlines or milestones to maintain urgency and momentum.
- Regular Review and Feedback – Goals should be revisited periodically, with ongoing feedback to adjust, refine, and reinforce progress.
Want to see these principles in action? Read: From Goal Setting to Goal-Achieving: A Guide to Winning with OKRs in Companies.
Understanding these core components is the first step; the next is seeing how well-crafted goals function in real-world performance.
What Good Goal Setting Looks Like
Effective goal setting transforms intentions into clear, actionable plans that yield tangible results. In fact, workers in small businesses who set daily goals produced 16% more, and firms saw a 13% increase in average labor output, even when goals were non-monetary. practical workers
Below, we examine the key elements and practical strategies that make goals effective and impactful.
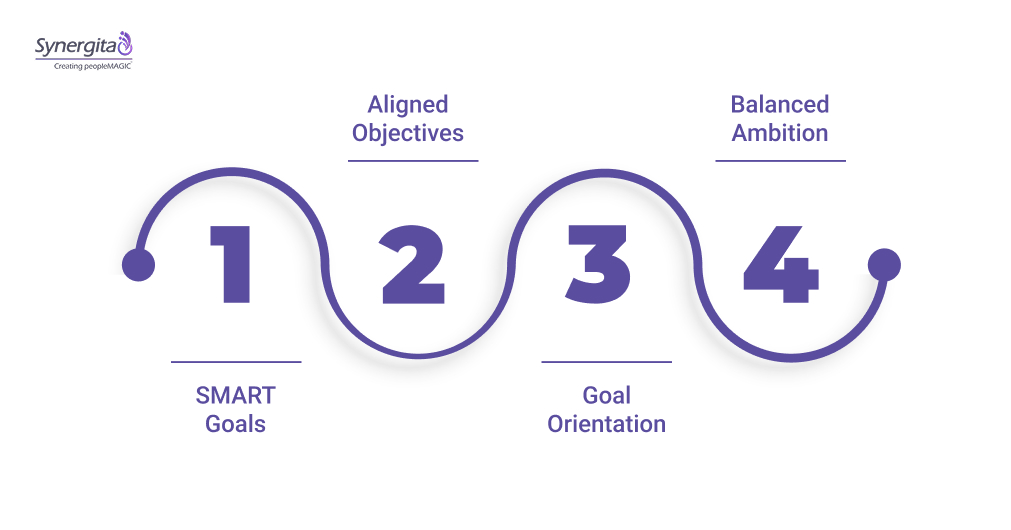
1. SMART Goals: Clear and Achievable Targets
The SMART framework ensures goals are:
- Specific: Clearly defined to avoid ambiguity. Instead of saying “Improve customer service”, a particular goal would be: “Answer 95% of customer support emails within 24 hours.”
- Measurable: Quantifiable to track progress. Rather than “Increase website traffic”, a measurable goal would be: “Increase monthly website visitors from 20,000 to 30,000 over the next quarter.”
- Achievable: Realistic and attainable. Instead of “Double sales in one month”, an achievable goal could be: “Increase monthly sales by 15% in the next quarter.”
- Relevant: Aligned with broader objectives. If the company wants to boost online engagement, an appropriate goal might be: “Publish three blog posts per week to improve social media shares and newsletter subscriptions.”
- Time-bound: Set within a clear timeframe. Instead of “Improve team productivity”, a time-bound goal would be: “Reduce project completion time by 10% within the next 90 days.”
This structure provides clarity and focus, making it easier to monitor progress and achieve desired outcomes.
2. OKRs: Ambitious and Aligned Objectives
Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) offer a strategic approach by:
- Setting inspirational objectives.Example: “Enhance the customer experience to become the most trusted brand in our segment.” This inspires the team to focus on meaningful impact rather than just completing tasks.
- Defining measurable key results to track progress.Example: For the objective above, key results could be:
- “Achieve a 90% customer satisfaction score in post-service surveys.”
- “Reduce average support ticket resolution time from 24 hours to 12 hours.”
OKRs encourage alignment across teams and foster a culture of transparency and accountability. They are particularly effective in dynamic environments where adaptability and innovation are crucial.
Suggested Read: The Secret to Hitting Bigger Goals Faster? Pairing OKRs with CFRs
3. Outcome-Oriented vs. Output-Oriented Goals
Not all goals are created equal; some focus on the results you want to achieve, while others track the tasks you complete.
Understanding the difference helps ensure effort translates into meaningful impact:
- Outcome-Oriented Goals focus on the desired impact or change, emphasizing the ‘why’ behind actions. For example, aiming to “increase customer satisfaction by 20% within six months” focuses on the result of improved service quality.
- Output-Oriented Goals concentrate on the activities or tasks completed, such as “conducting 50 customer feedback surveys.” While outputs are necessary, they should lead to meaningful outcomes to ensure effectiveness.
Balancing both approaches ensures that efforts translate into tangible results.
4. Balancing Realism with Stretch Goals
Setting goals that are both achievable and challenging is key:
- Realistic Goals are attainable and provide a sense of accomplishment.
- Stretch Goals push boundaries and encourage innovation, though they should remain within the realm of possibility to maintain motivation.
Striking the right balance between these types of goals can drive continuous improvement and engagement.
Now, with a clear understanding of what makes goals effective, it’s time to see how they work in practice.
Examples and Best Practices to Implement Goal Setting
Seeing different types of goals shows how structured objectives boost performance. Research by Latham and Locke found that goal setting can increase productivity by 11% to 25%, resulting in an additional two hours in an eight-hour day, demonstrating the importance of applying the right approach.
The following outlines key goal types and best practices for effective implementation.
1. Customer Service Representative: Enhancing Response Times
Customer service is often the first point of contact with clients, and delays in response can negatively impact satisfaction and loyalty. Setting a goal, such as reducing the average email response time to under two hours, ensures that representatives prioritize prompt and consistent communication.
Best Practice:
Define goals that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Focus on the outcome (customer satisfaction) rather than just the activity (answering emails).
Implementation:
- Training: Equip staff with strategies to manage high volumes of emails efficiently.
- Tools: Use automated sorting, tagging, and prioritization software to streamline workflow.
- Monitoring & Feedback: Track response times daily and provide regular feedback to highlight areas for improvement.
2. Sales Team: Increasing Conversion Rates
For sales teams, it’s not enough to contact leads; they need to convert them into paying customers. Setting goals focused on increasing conversion rates helps salespeople prioritize high-potential prospects, refine their pitch, and focus on strategies that actually drive revenue growth.
Best Practice:
Link sales goals to organizational objectives. Ensure goals are challenging yet achievable, and include measurable metrics such as percentage increases or revenue targets.
Implementation:
- Lead Qualification: Implement processes to identify prospects with the highest likelihood of conversion.
- Skill Development: Offer targeted sales training on closing techniques and handling objections.
- Tracking: Use CRM tools to monitor conversions, identify bottlenecks, and adjust strategies as needed.
3. Marketing Team: Boosting Social Media Engagement
Marketing success isn’t only measured by output, such as posts or campaigns; it’s about engagement and meaningful interaction. Setting a goal to increase engagement by a defined percentage compels the team to create content that resonates with the audience, drives meaningful discussions, and fosters brand loyalty.
Best Practice:
Set goals tied to both measurable metrics (likes, shares, comments) and business outcomes (brand awareness, lead generation).
Implementation:
- Content Planning: Create a content calendar that includes topics appealing to your audience and encourages interaction.
- Analytics: Track engagement metrics using analytics tools to identify which content performs best.
- Campaign Testing: Run A/B tests on posts or campaigns to optimize performance.
4. Human Resources: Improving Employee Retention
Employee turnover is costly and disruptive. Setting retention goals helps HR focus on the strategies that improve workplace satisfaction and engagement, ensuring that talented staff stay longer and contribute meaningfully to company objectives.
Best Practice:
Align HR goals with the organization’s culture and strategic priorities. Focus on both preventive measures (improving satisfaction) and proactive actions (development and recognition).
Implementation:
- Feedback Mechanisms: Conduct regular surveys and one-on-one sessions to identify issues early.
- Development Programs: Offer training, mentorship, and career growth opportunities.
- Recognition: Implement rewards and recognition systems to reinforce positive behaviors.
5. Product Development: Accelerating Time-to-Market
Speed is critical in product development; delays can allow competitors to capture market share. Goals that focus on reducing time-to-market encourage teams to streamline processes, remove bottlenecks, and prioritize high-impact work without compromising quality.
Best Practice:
Set ambitious but realistic targets for development cycles. Strike a balance between speed and quality to maintain customer trust and satisfaction.
Implementation:
- Process Optimization: Map workflows to identify inefficiencies.
- Collaboration Tools: Use project management software for task tracking and communication.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Encourage collaboration between development, design, and marketing for faster decision-making.
From improving customer response times to accelerating product launches, effective goal setting drives real results. Synergita helps you put these practices into action with AI-powered support and clear analytical reports, so you can track OKR progress accurately without being distracted by vanity metrics.
While these examples demonstrate the effectiveness of goal setting, even well-designed goals can encounter obstacles. Recognizing common challenges helps ensure your goals truly deliver results.
Challenges in Goal Setting
Even well-designed goals can encounter obstacles that hinder their effectiveness. Recognizing these common challenges and implementing practical workarounds to address them enables organizations to prevent setbacks, maintain alignment, and ensure that goals translate into measurable results.
The table below highlights common goal-setting challenges and practical strategies to overcome them.
| Challenge | Why It Happens | Workaround |
|---|---|---|
| Unclear Goals | Goals are vague or ambiguous | Use SMART goals; break large objectives into clear, actionable tasks |
| Lack of Motivation | Goals feel irrelevant or uninspiring | Align goals with personal/team priorities; celebrate small wins |
| Overwhelming Complexity | Goals seem too big or daunting | Break into smaller tasks; prioritize using GROW or similar frameworks |
| Unrealistic Expectations | Goals are too ambitious | Ensure goals are achievable; adjust based on resources and capacity |
| Poor Planning | No clear roadmap to achieve goals | Create step-by-step plans; use Gantt charts or project management tools |
| Time Management Issues | Tasks take longer than expected | Use time-blocking or Pomodoro; focus on high-priority tasks |
| Lack of Accountability | No one checks progress | Share goals with mentor/team; schedule regular check-ins |
| Fear of Failure | Anxiety prevents action | Focus on progress over perfection; set process-oriented goals |
| Inconsistent Reviews | Goals become outdated or misaligned | Schedule regular progress reviews; adjust goals as needed |
| External Distractions | Interruptions derail focus | Minimize distractions; create dedicated work time and use focus tools |
Once goals are set and challenges addressed, it’s essential to measure outcomes and adapt the process for continuous improvement.
Measuring and Evolving the Process
Setting goals is just the first step; tracking progress and refining them ensures objectives stay relevant and effective. Here’s how organizations can measure progress and improve the goal-setting process:
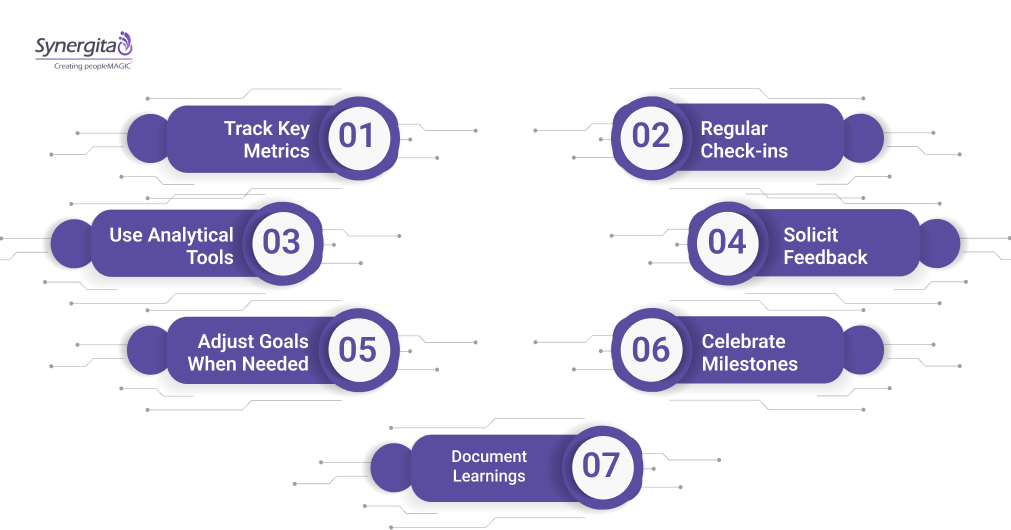
- Track Key Metrics: Identify performance indicators aligned with each goal, whether quantitative (such as sales, productivity, or response times) or qualitative (such as customer satisfaction or employee engagement).
- Regular Check-ins: Schedule weekly or monthly reviews to assess progress, discuss challenges, and make course corrections before goals go off track.
- Use Analytical Tools: Leverage dashboards or softwares like Synergita to visualize progress, identify trends, and pinpoint bottlenecks in real-time.
- Solicit Feedback: Collect input from team members and stakeholders to understand obstacles, refine goals, and improve processes.
- Adjust Goals When Needed: Be flexible; update targets, timelines, or strategies as needed to accommodate changing priorities, performance data, or organizational needs.
- Celebrate Milestones: Recognize achievements along the way to maintain motivation and reinforce positive behaviors.
- Document Learnings: Capture insights from successes and setbacks to improve future goal-setting cycles and build organizational knowledge.
With progress measured and insights in hand, the next step is using these learnings to drive smarter, more effective goal management across the organization.
Driving Smarter Goal Management
Even with clear goals, organizations often struggle to turn objectives into results. Teams lose focus, progress goes untracked, and valuable insights get buried in disconnected tools, slowing performance and leaving leaders unsure whether their strategies are working. Effective goal management requires tracking, alignment, and actionable insights without wasting time on scattered data.
Synergita solves this with AI-powered support and clear analytical reports that highlight OKR progress and eliminate vanity metrics. Teams can monitor performance in real time, make quick course corrections, and stay aligned with organizational objectives. The result is increased productivity, improved focus, and a measurable impact.
See it in action: book a Synergita demo today!
FAQs
1. What is goal setting in performance management?
It’s the process of defining, tracking, and aligning individual and team objectives with organizational priorities to drive performance.
2. Why is goal setting important for employee productivity?
Clear, actionable goals provide focus, motivation, and measurable outcomes, boosting productivity and engagement.
3. What are common challenges in goal setting?
Challenges include unclear goals, lack of motivation, unrealistic targets, poor planning, and inconsistent reviews.
4. How do OKRs differ from traditional goals?
OKRs focus on ambitious objectives paired with measurable key results, promoting alignment, transparency, and accountability.
5. How can organizations streamline goal management?
Tools like Synergita provide AI-powered insights, progress tracking, and analytical reports to simplify goal management and improve outcomes.



